Scientific Image Gallery
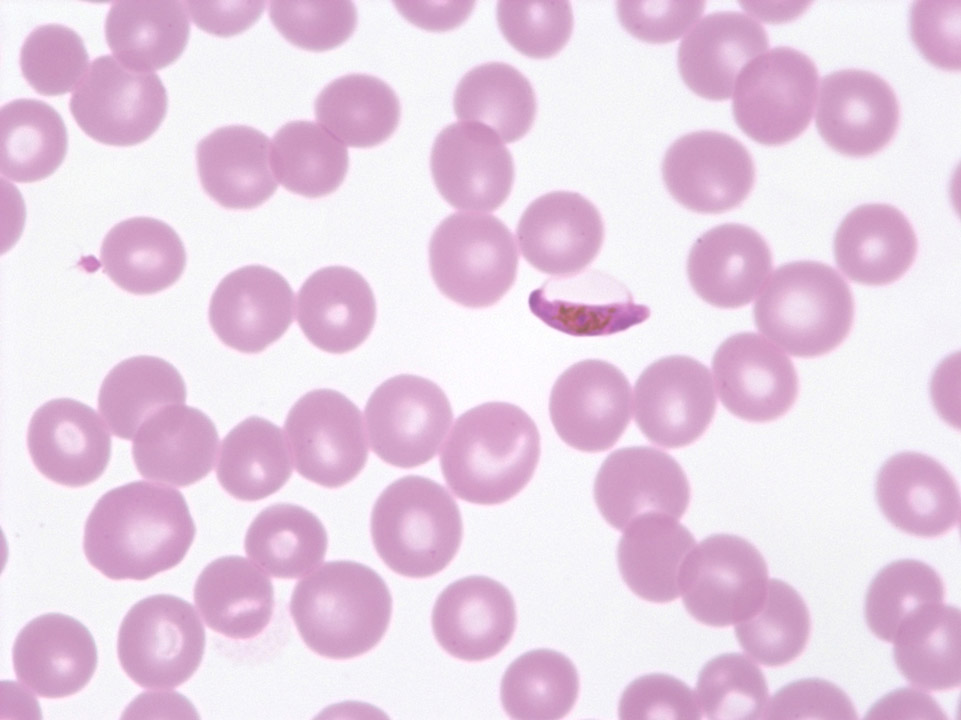
Fragmented red blood cells and thrombocytopenia in the case of a thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP). In the partially thrombosed capillaries the red blood cells are exposed to a high degree of shearing force, which causes them to burst.
<p>Fragmented red blood cells and thrombocytopenia in the case of a thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP). In the partially thrombosed capillaries the red blood cells are exposed to a high degree of shearing force, which causes them to burst.</p>
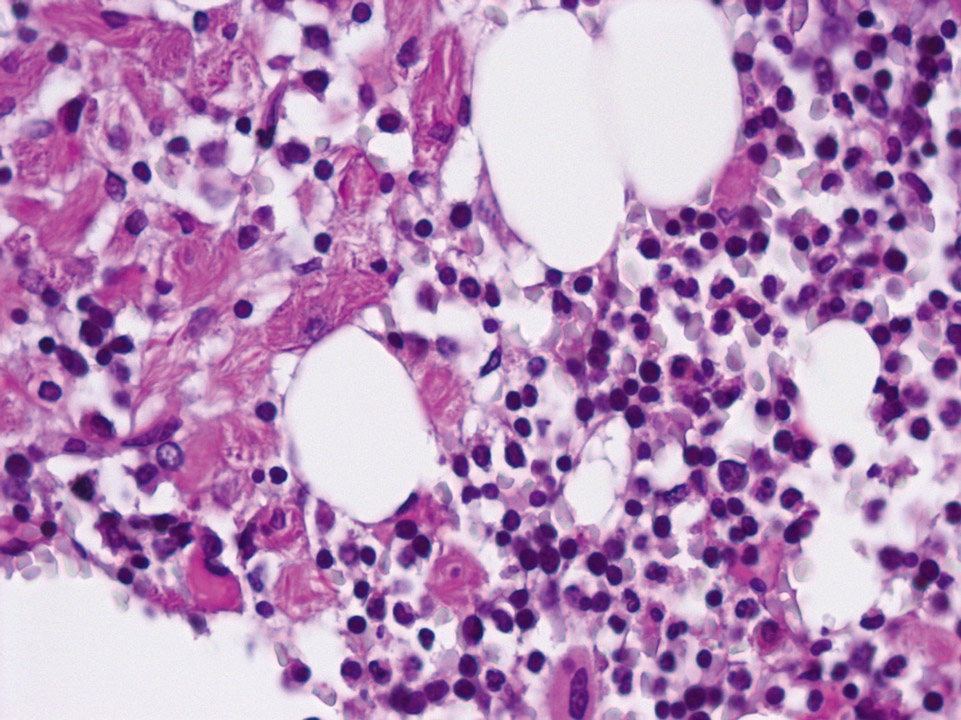
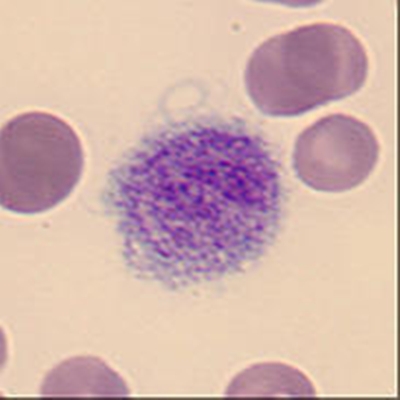
Bone marrow histology (periodic acid Schiff stain, PAS) displaying macrophages on the left, with a cytoplasm resembling crinkled parchment. They are so-called 'Gaucher' cells. Gaucher's disease is characterised by a congenital defect of the enzyme glucocerebrosidase leading to an increase of certain glycolipids (cerebrosides) inside the macrophages. On the right side of the picture the bone marrow appears normal.
<p>Bone marrow histology (periodic acid Schiff stain, PAS) displaying macrophages on the left, with a cytoplasm resembling crinkled parchment. They are so-called 'Gaucher' cells. Gaucher's disease is characterised by a congenital defect of the enzyme glucocerebrosidase leading to an increase of certain glycolipids (cerebrosides) inside the macrophages. On the right side of the picture the bone marrow appears normal.</p>
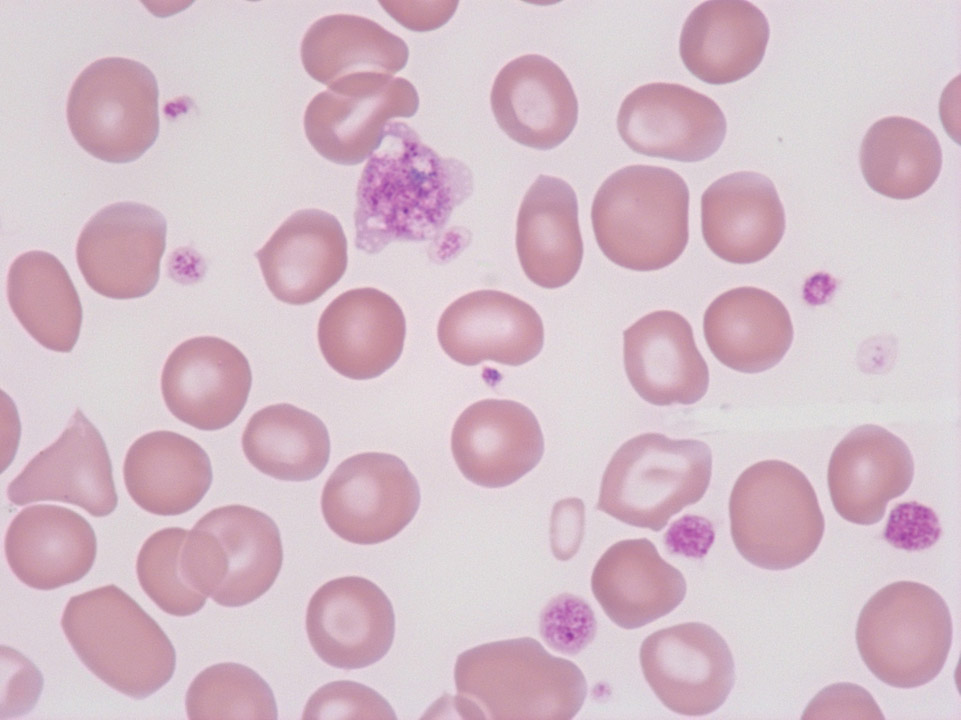
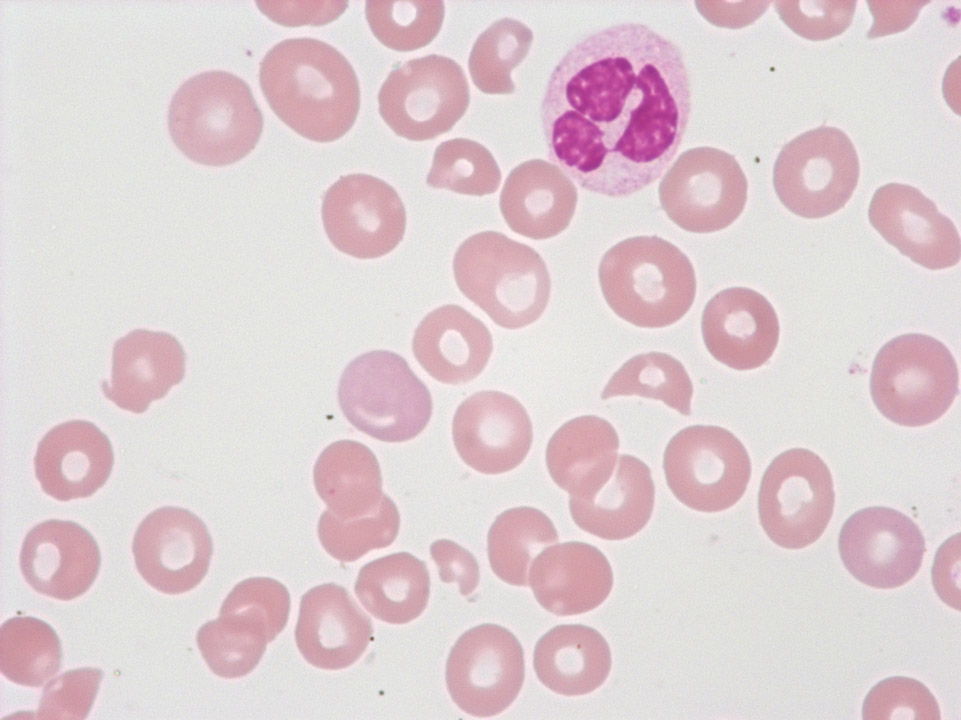
Giant platelet with prominent granulation from a patient with essential thrombocythaemia (ET). (Defective haematopoiesis causes detectable poikilocytosis.)
<p>Giant platelet with prominent granulation from a patient with essential thrombocythaemia (ET). (Defective haematopoiesis causes detectable poikilocytosis.)</p>
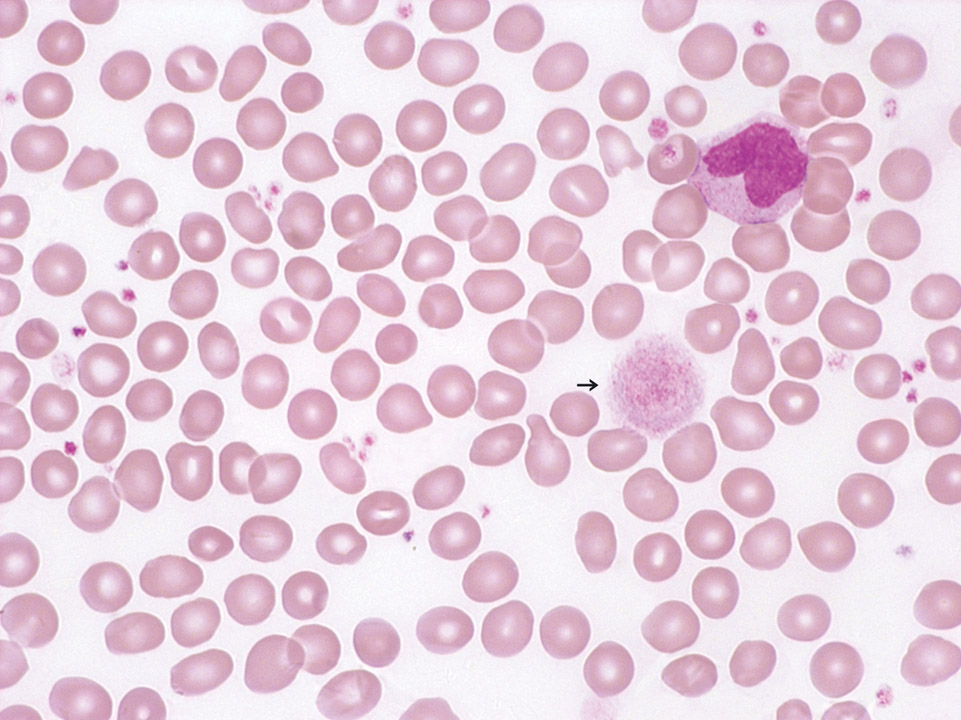
Peripheral blood (May-Grünwald-Giemsa stain) of a patient with essential thrombocythaemia, ET. Giant platelets (->) are frequently observed in this disease.
<p>Peripheral blood (May-Grünwald-Giemsa stain) of a patient with essential thrombocythaemia, ET. Giant platelets (->) are frequently observed in this disease.</p>
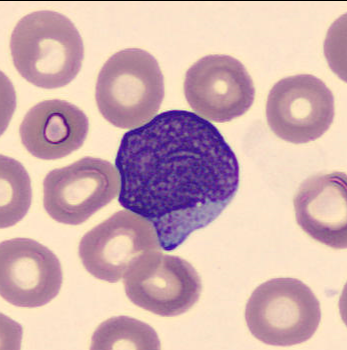
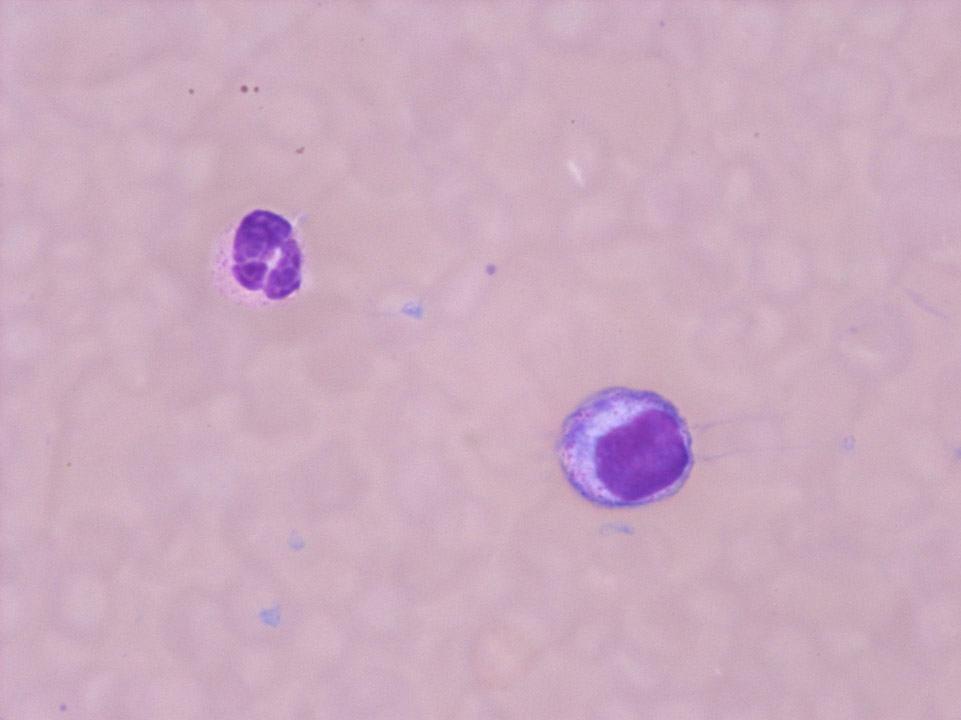
Granulated blasts have a size of 12 - 16 µm and show significant reddish granules in their cytoplasm. The shape of the nucleus is round or oval with a very high nucleocytoplasmic ratio of 70 – 95%.
The chromatin is predominantly regularly distributed and neither clumped nor condensed. The nucleus has a varying number of nucleoli which may be hidden by the chromatin.
<p>Granulated blasts have a size of 12 - 16 µm and show significant reddish granules in their cytoplasm. The shape of the nucleus is round or oval with a very high nucleocytoplasmic ratio of 70 – 95%. </p> <p>The chromatin is predominantly regularly distributed and neither clumped nor condensed. The nucleus has a varying number of nucleoli which may be hidden by the chromatin. </p>
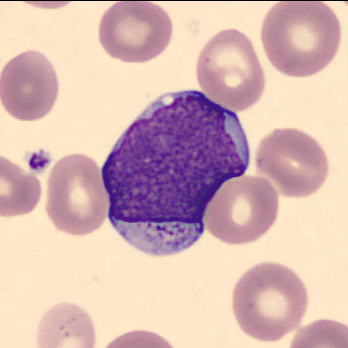
Granulated blasts have a size of 12 – 16 µm and show significant reddish granules in their cytoplasm. The shape of the nucleus is round or oval with a very high nucleocytoplasmic ratio of 70 – 95%.
The chromatin is predominantly regularly distributed and neither clumped nor condensed. The nucleus has a varying number of nucleoli which may be hidden by the chromatin.
<p>Granulated blasts have a size of 12 – 16 µm and show significant reddish granules in their cytoplasm. The shape of the nucleus is round or oval with a very high nucleocytoplasmic ratio of 70 – 95%. </p> <p>The chromatin is predominantly regularly distributed and neither clumped nor condensed. The nucleus has a varying number of nucleoli which may be hidden by the chromatin. </p>